# 前端面试题
# 1. 箭头函数不适合的场景有哪些,为什么?
- 不适合做对象的方法
- 不能作为构造函数
- 不能定义原型方法
因为箭头函数不绑定 this,以上场景都需要动态绑定 this,所以不适合使用箭头函数。
# 2. this 作用场景哪些,并分别指代什么?
- 默认绑定,非严格模式,this 执行 window, 严格模式,this 指向 undefined
- 对象的方法,this指向对象
- 构造函数,this 指向实例对象
- 显示绑定,call,bind,apply 方法显示指定 this
# 3. promise 是什么,有哪些特点?
Promise 是异步编程的一种解决方案,简单说是一个容易,保存着某个未来结束的事件的结果。promise 是一个对象,有两个特点:
- Promise对象的状态不受外界影响。promise 对象有三种状态:pending(进行中),fulfilled(已成功),rejected(已失败)。
- 一旦状态改变,就不会再变,任何时候都可以得到这个结果。promise对象的状态改变只有两种可能,从pending 到 fulfilled,从 pending到 rejected.
Promise的缺点:
- 无法取消 promise,一旦创建成功就会立即执行,无法中途取消。
- 如果不设置回调函数,promise 内部抛出的错误不会反映到外部。
- 当处于 pending 状态,无法得知进度。
# 4.MVVM 和 MVC 的区别
MVC模式在概念上强调 Model, View, Controller 的分离,各个模块也遵循着由 Controller 来处理消息,含事件响应,Model 掌管数据源,View 负责资料显示的职责分离原则。
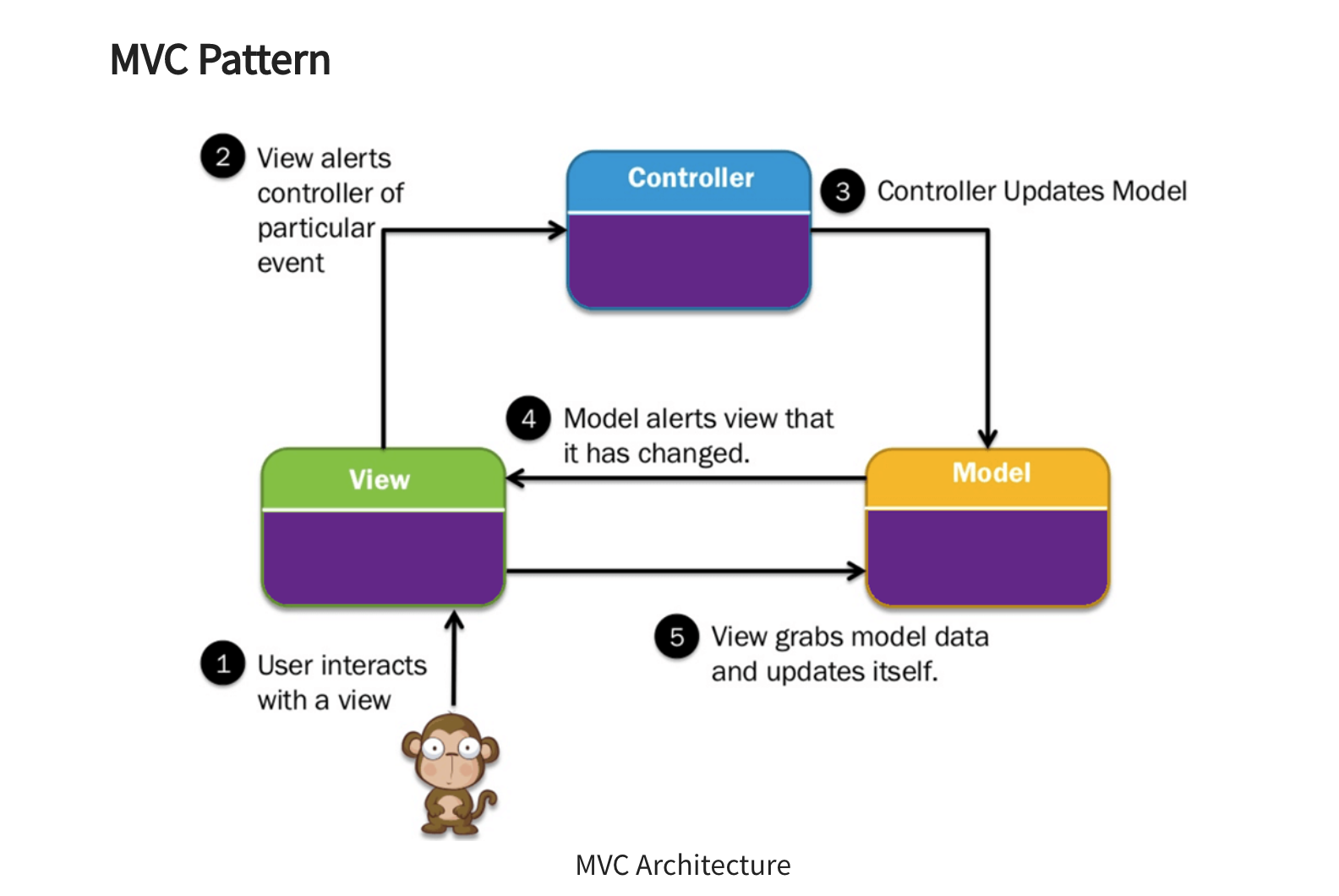
# Model
The model component stores data and related logic. It represents data that is being transferred between controller components or any other related business logic.
For example, a Controller object helps you to retrieve the customer info from the database. It manipulates data and sends it back to the database or use it to render the same data.
# View
A View is that part of the Application that represents the presentation of data. Views are created by the data gathered from the model data. A view requests the Model to give information so that it resents the output to the user.
The View also represents the data from charts, diagrams, and table. For example, any customer view will include all the UI components like text boxes, dropdowns, etc.
# Controller
The Controller is that part of the Application that handles the user interaction. The Controller interprets the mouse and keyboard inputs from the user, informing the Model and the View to change as appropriate.
A Controller sends commands to the Model to update its state(E.g., Saving a specific document). The Controller also sends commands to its associated view to change the View's presentation (For example, scrolling a particular document).
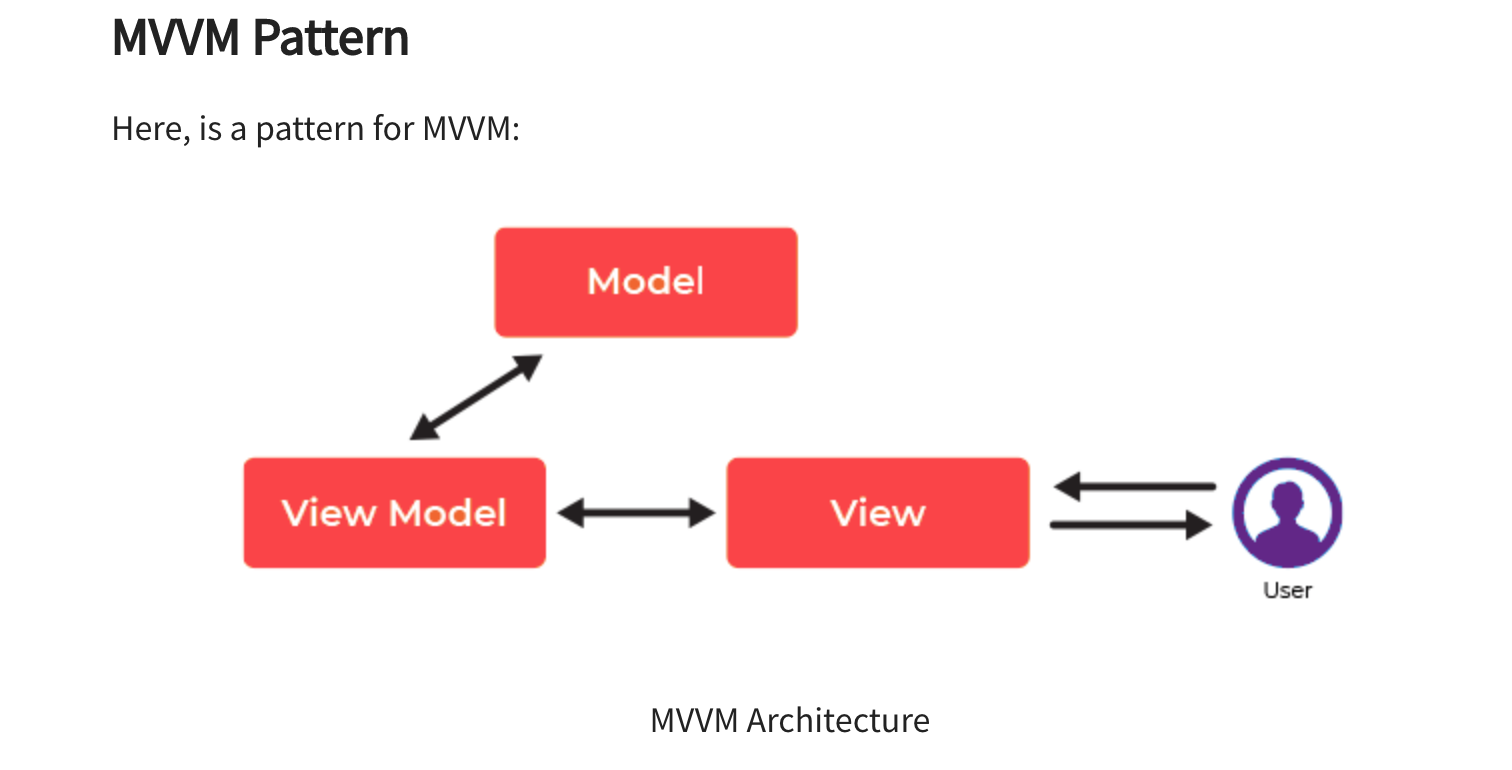
# Model
The model stores data and related logic. It represents data that is being transferred between controller components or any other related business logic.
For example, a Controller object will retrieve the student info from the school database. It manipulates data and sends it back to the database or use it to render the same data.
# View:
The View stands for UI components like HTML, CSS, jQuery, etc. In MVVC pattern view is held responsible for displaying the data which is received from the Controller as an outcome. This View is also transformed Model (s) into the User Interface (UI).
# View Model:
The view model is responsible for presenting functions, commands, methods, to support the state of the View. It is also accountable to operate the model and activate the events in the View.
# Difference between MVVM and MVC
Here, are the important difference between MVVM and MVC
| MVC | MVVM |
|---|---|
| Controller is the entry point to the Application. | The view is the entry point to the Application. |
| One to many relationships between Controller & View. | One to many relationships between View & View Model. |
| View Does not have reference to the Controller | View have references to the View-Model. |
| MVC is Old Model | MVVM is a relatively New Model. |
| Difficult to read, change, to unit test, and reuse this Model | The debugging process will be complicated when we have complex data bindings. |
| MVC Model component can be tested separately from the user | Easy for separate unit testing and code is event-driven. |